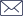
Gas engines are highly efficient at providing the stimulus for the growth of plants, whilst in parallel providing a flexible supply of electrical power. Heat, light and carbon dioxide (CO2) all promote plant growth. Gas engines provide electrical power at the alternator and when in a cogeneration configuration can also recover useful heat. Carbon dioxide is released in the exhaust gases of the engine as a by-product of the combustion of the fuel gas. Electrical power can be used to provide energy for lighting or can be exported to the grid, heat can be stored as hot water for use when needed and finally the CO2 can be scrubbed and used to promote plant growth.
Benefits
» Efficiency levels up to 95%, therefore high contribution to resource conservation and maximization of profits
» Provides power to grid at times of maximum demand hence receiving highest power sale prices
» Time-independent supply of CO2 and heat through heat storage
» High quality CO2
Carbon Dioxide & Plant Growth
Plants grow by converting CO2 to carbon through photosynthesis. Air generally contains approximately 350 ppm CO2. Optimal CO2 levels depend on the type of plant and generally lie above 700 ppm. With increased artificial lighting, as present in greenhouses, plants absorb even more CO2. If the greenhouse atmosphere is enriched with CO2, the temperature kept on a constant level and sufficient lighting, provided plant growth and consequently the harvest yield can be increased significantly. When burning natural gas in gas engines, approximately 0.2kg CO2 is produced be kWh of energy input. This CO2 is present in the exhaust of gas engines in a concentration approximately 5-6% by volume.
Energy Usage
The energy created by gas engine cogeneration / combined heat and power systems in greenhouses can be used in various ways. The electricity can provide the power for the artificial lighting and/or be fed into the electricity grid. The heat efficiently meets the greenhouse’s requirements. In addition, the climate-relevant CO2of the engine exhaust gas serves as a fertiliser for the plants.
Exhaust Purification
After the purification of the exhaust gas with special catalytic converters (SCR and oxidation catalytic converters), the exhaust gas is cooled down by a heat exchanger to approximately 55°C and supplied to the greenhouse for CO2enrichment. A measurement device that constantly measures the exhaust gas levels ensures maximum safety for vegetation.
Key Figures
Efficient operation is possible with approximately 1 hectare or larger greenhouse areas
» CO2 fertilisation is suitable for nearly all plant types
» CO2 fertilisation with simultaneously heat supply: dimensioning for 0.5MWel/ha
» CO2 fertilisation with simultaneous heat supply and illumination dimensioning for 0.35 MWel/ha
» Illumination suitable for vegetables (e.g. tomatoes or peppers) and for flowers (e.g. chrysanthemums or roses)
» The decisive factors for economical plant operation are the high electrical efficiency, combined with the usage of heat and CO2 fertilisation.
If you would like to discuss your greenhouse cogeneration project in more depth, please contact us.
Benefits
» Efficiency levels up to 95%, therefore high contribution to resource conservation and maximization of profits
» Provides power to grid at times of maximum demand hence receiving highest power sale prices
» Time-independent supply of CO2 and heat through heat storage
» High quality CO2
Carbon Dioxide & Plant Growth
Plants grow by converting CO2 to carbon through photosynthesis. Air generally contains approximately 350 ppm CO2. Optimal CO2 levels depend on the type of plant and generally lie above 700 ppm. With increased artificial lighting, as present in greenhouses, plants absorb even more CO2. If the greenhouse atmosphere is enriched with CO2, the temperature kept on a constant level and sufficient lighting, provided plant growth and consequently the harvest yield can be increased significantly. When burning natural gas in gas engines, approximately 0.2kg CO2 is produced be kWh of energy input. This CO2 is present in the exhaust of gas engines in a concentration approximately 5-6% by volume.
Energy Usage
The energy created by gas engine cogeneration / combined heat and power systems in greenhouses can be used in various ways. The electricity can provide the power for the artificial lighting and/or be fed into the electricity grid. The heat efficiently meets the greenhouse’s requirements. In addition, the climate-relevant CO2of the engine exhaust gas serves as a fertiliser for the plants.
Exhaust Purification
After the purification of the exhaust gas with special catalytic converters (SCR and oxidation catalytic converters), the exhaust gas is cooled down by a heat exchanger to approximately 55°C and supplied to the greenhouse for CO2enrichment. A measurement device that constantly measures the exhaust gas levels ensures maximum safety for vegetation.
Key Figures
Efficient operation is possible with approximately 1 hectare or larger greenhouse areas
» CO2 fertilisation is suitable for nearly all plant types
» CO2 fertilisation with simultaneously heat supply: dimensioning for 0.5MWel/ha
» CO2 fertilisation with simultaneous heat supply and illumination dimensioning for 0.35 MWel/ha
» Illumination suitable for vegetables (e.g. tomatoes or peppers) and for flowers (e.g. chrysanthemums or roses)
» The decisive factors for economical plant operation are the high electrical efficiency, combined with the usage of heat and CO2 fertilisation.
If you would like to discuss your greenhouse cogeneration project in more depth, please contact us.